publication date: Sep 9, 2021
|
author/source: SCION Instruments

Introduction
In Gas Chromatography there are three gases that are commonly used as a carrier gas: nitrogen, helium and hydrogen. The importance of carrier gas selection has been a discussion point amongst the users of Gas Chromatography for many years. When selecting the right carrier gas the user has to consider different parameters such as; price, performance, speed, analytical compatibility or just availability.

Background
When choosing the right carrier gas it shows that all the available gases have pros and cons. Helium is one of the most common elements and is used in a wide range of markets applications including laboratory applications such as GC. This carrier gas is produced as a by product from the extraction of natural gas, due to increasing demand of growing economies world wide, not all of the markets demand can be covered. Unfortunately this leads to helium shortages and results in increasing prices. In addition the environmental impact should also be considered. Helium can not be re-used or manufactured, meaning that with every use we are depleting the world’s resources of helium. Hydrogen is considered the most optimal choice, combining high efficiency separations with short analysis times and on top of that it can be produced by a generator. The biggest issue using hydrogen gas is the safety risk, a 4% concentration in air can lead to an explosion. Nitrogen has a low optimum of linear velocity and therefore the analysis will take longer, however it should be kept in mind that this is a highly efficient carrier gas . A big advantage of nitrogen is that it can be directly generated from air, this means that it is readily available. The efficiency comparison between these gases Is given by the van Deemter curve which relates the plate height (efficiency) with carrier gas velocity through the column (speed), as shown in figure 1.
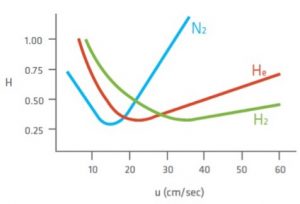
Figure 1: Van Deemter curve
Example
A good practical example using different carrier gases is the Scion Cannabis Potency application (AN092, 093 and 130), these applications all use the same column and the same GC conditions. These applications show that nitrogen in comparison to helium and hydrogen is the slower carrier gas. Figure 2 shows the chromatogram of Cannabidiol (CBD) using different carrier gases.
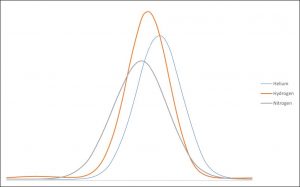
Figure 2: Chromatogram of CBD using different carrier gases.
To compare the peak shapes with each other it is important that all examples are around the same area.
| |
Helium |
Hydrogen |
Nitrogen |
| Area |
703 |
690 |
700 |
| Peak height |
49227 |
53608 |
40987 |
| AS 4.4% |
1.07 |
1.0 |
0.92 |
| AS 10% |
1.08 |
1.0 |
0.90 |
Table 1: CBD data for the different carrier gases
When looking at the data in table 1 it shows that hydrogen has the most symmetrical peak shape. Although Helium and Nitrogen are less symmetrical these carriers are still excellent gases to perform identification and quantification with.
Conclusion
Hydrogen, Helium and Nitrogen are all gases that can be used as a carrier gas for gas chromatography. When choosing the right carrier gas not only the quality and speed of the analysis should be kept in mind but also the costs. Hydrogen and nitrogen are both gases that are less expensive and both can be produced on site. If you need help choosing the right carrier gas for your application or if you need optimization of the method please contact our pre-sales experts. All analysis shown in this application note were performed with a Scion 4X6-GC analyser equipped with a split/spitless injector, Scion Instruments column and FID.
Download Application Note
Download the complete application note: Carrier Gases and their Differences
News Channels
Subscribe to any of our newsletters for the latest on new laboratory products, industry news, case studies and much more!

Request your free copies HERE
Popular this Month
Top 10 most popular articles this month
Today's Picks
Looking for a Supplier?
Search by company or by product
Please note Lab Bulletin does not sell, supply any of the products featured on this website. If you have an enquiry, please use the contact form below the article or company profile and we will send your request to the supplier so that they can contact you directly.
Lab Bulletin is published by newleaf marketing communications ltd.